Before knowing analog and digital signals, first, let’s see what is signal?
Table of Contents
What is Signal?
A Signal is an electromagnetic wave that is used to communicate system-to-system by sending data from one network to another network is basically known as “Signal”.
In a computer network there are mainly two types of signals are:
- Analog Signal
- Digital Signal
What is Analog Signal?
An Analog signal is a signal which is continuous and has a time-varying feature. It is a representation of time-varying quantity. For example, the Human voice can be considered an analog signal because the signal of the human voice flows in a continuous manner.
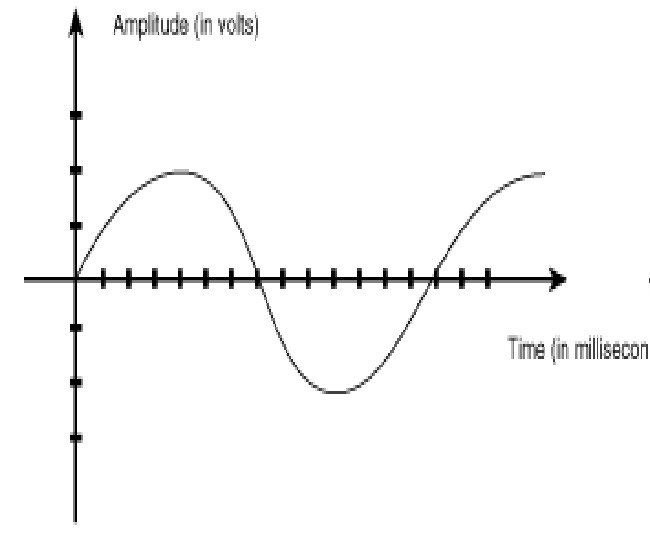
In other words, we can say that the analog signal is represented by the continuous variable which transmits the information/data as a response to physical phenomenon. It is known as an “Analog Signal”
Examples of digital signals are Temperature, Pressure, Flow Measurement, etc.
Types of Analog Signal
- Simple Analog Signal
- Composite Analog Signal
What is Digital Signal?
As the word suggests “Digital” which means it describes the electronic technology that generates signals. It is a physical signal that is represented by two discrete values “0” & “1”, these discrete values are known as bitstream.
(If you want to know more about these discrete values then you should read our this article: What is the difference Between Bit and Byte?
In simple words, we can say that the binary signals are known as “Digital signals” where the signals are converted into a small bit form which is represented by a series of “0” & “1”.
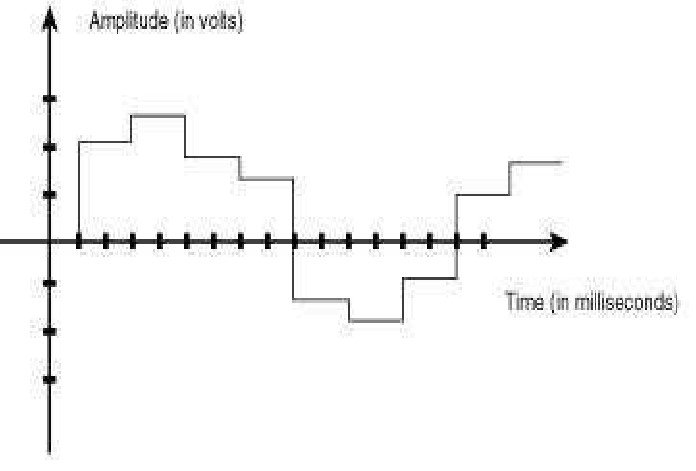
Examples of digital signals are Motor, Digital Phones, Digital pens, etc
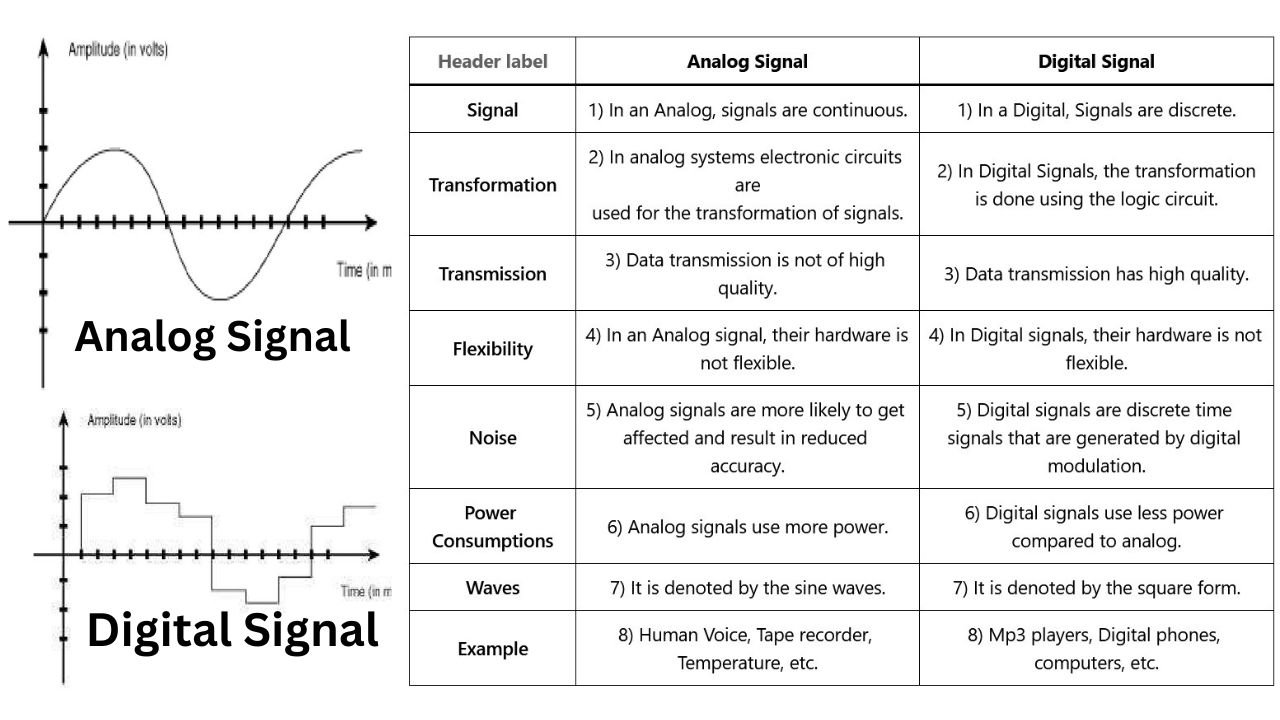
Difference between Analog and Digital Signal
| Analog Signal | Digital Signal | |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | 1) In an Analog, signals are continuous. | 1) In a Digital, Signals are discrete. |
| Transformation | 2) In analog systems electronic circuits are used for the transformation of signals. | 2) In Digital Signals, the transformation is done using the logic circuit. |
| Transmission | 3) Data transmission is not of high quality. | 3) Data transmission has high quality. |
| Flexibility | 4) In an Analog signal, their hardware is not flexible. | 4) In Digital signals, their hardware is not flexible. |
| Noise | 5) Analog signals are more likely to get affected and result in reduced accuracy. | 5) Digital signals are discrete time signals that are generated by digital modulation. |
| Power Consumptions | 6) Analog signals use more power. | 6) Digital signals use less power compared to analog. |
| Waves | 7) It is denoted by the sine waves. | 7) It is denoted by the square form. |
| Example | 8) Human Voice, Tape recorder, Temperature, etc. | 8) Mp3 players, Digital phones, computers, etc. |