Table of Contents
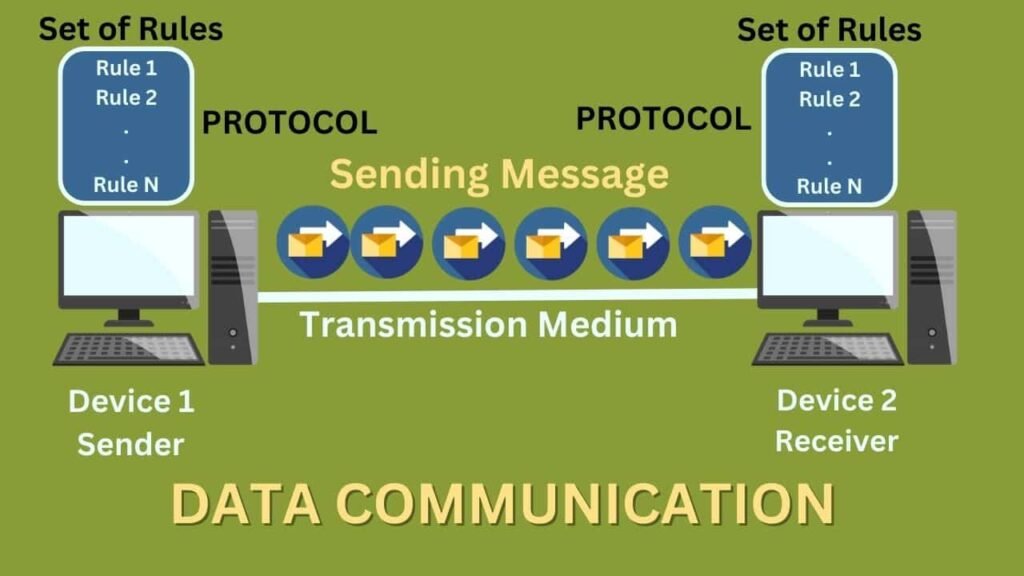
Data Communication
As the name suggests “Data Communication” means the communication of data b/w the devices, It is the process of sending data/messages over the network to the receivers known as “Data Communication”.
In Data communication when two devices are connected over the network for communication like suppose there is a Device A and Device B. In contrast, Device A is Sender and Device B is the receiver. These two devices are connected with a cable or a wireless mode it depending upon the transmission medium that we used to connect these devices. Now, Device A is able to send some messages to Device B, and the message can be in any form like text, audio, etc. It is basically known as “Data Communication”.
Components of Data Communication
There are mainly five components that explain the total process of data communication:
- Sender
- Receiver
- Message
- Transmission Medium
- Protocol
Sender
Basically, a Sender is a device that sends some data or can say messages to the receiver. The messages can be in any form like text messages, audio messages, video messages, photos, documents messages, etc. A sender is also known as a source, transmitter, or node.
Receiver
The receiver is also a device where it performs the process of receiving messages known as the Receiver. The sender device location is typically different from the receiver device location.
Message
In our daily life, we send messages to our friends, relatives, and to our family through Instagram, WhatsApp, SMS, and Facebook platforms. And the message may be in any form like text, image, video clip, documents, etc. This is basically known as “Message”.
In short, we can say the message or data that can be sent from the sender to the receiver is known as “Message”.
Transmission Medium
When the sender sends the messages to the receiver, there is a path or can say medium to travel the data to the receiver. These mediums can be a wired path or a wireless path. A wired path like coaxial cable, fiber-optic cables, etc., and a wireless path like radio waves and laser, etc.
Protocol
Protocol is basically a set of rules that defines how the data will be transmitted between the devices. A protocol is required in data communications; otherwise, the communicating entities are equivalent for both parties when they are trying to communicate in a foreign language without knowing the other language.
Types of Data Communication (Modes of Transmission)
Three types of Data Communication are there:
- Simplex Mode of Communication
- Half-Duplex Mode of Communication
- Full-Duplex Mode of Communication
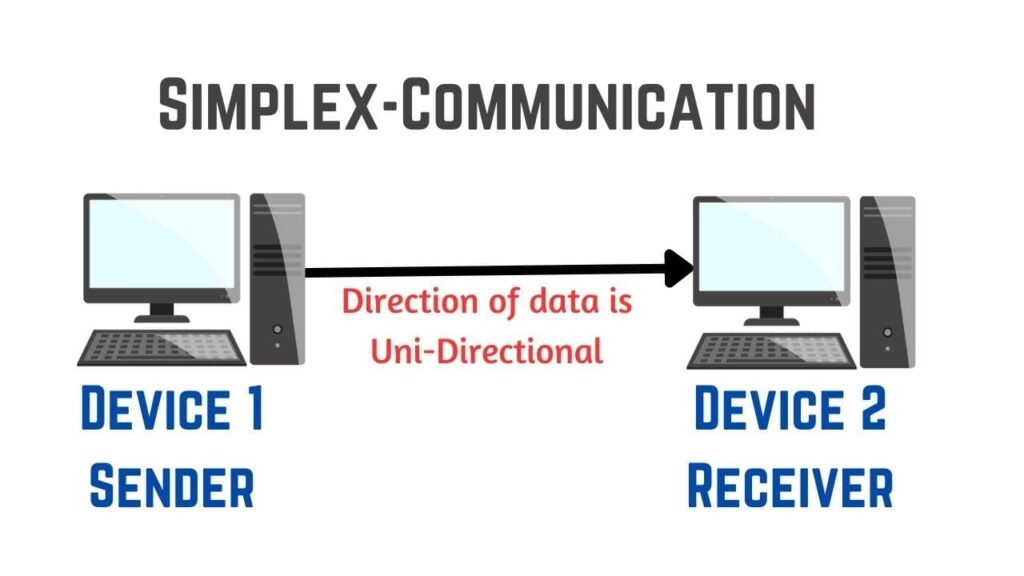
Simplex Communication
In this type of communication, data or message can be sent only in a one direction or can say uni-directional communication in which the one device only receives data and another device only transmits data, and each device utilises its entire transmission capacity.
Example: Keyboard, Monitor, LoudSpeaker etc.
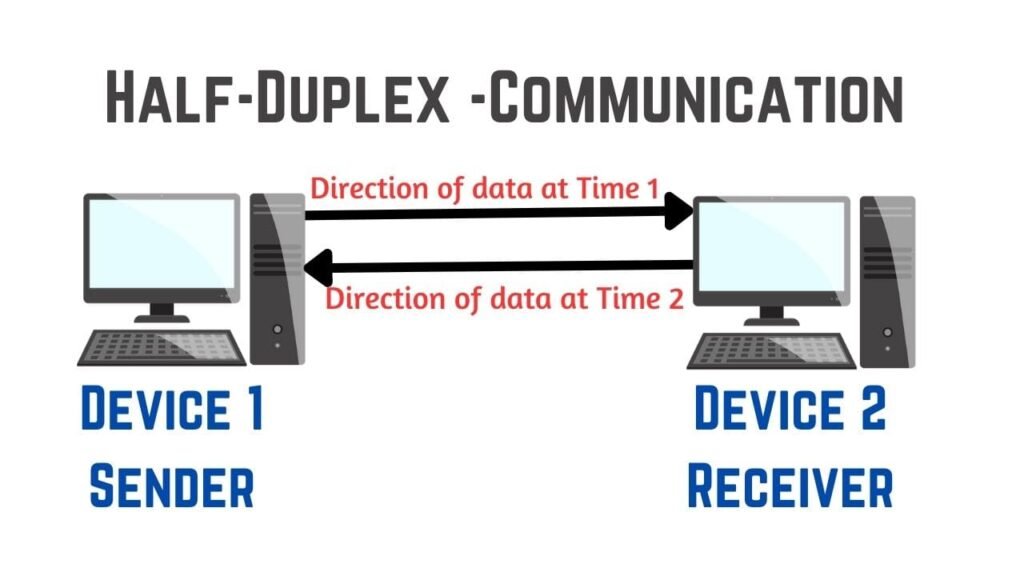
Half-Duplex Communication
In this types of communication, a sender can able to send the data or message to the receivers and also the receivers receives the data but not at the same time. It is called two-way communication or bidirectional communication.
Example: walkie-talkie
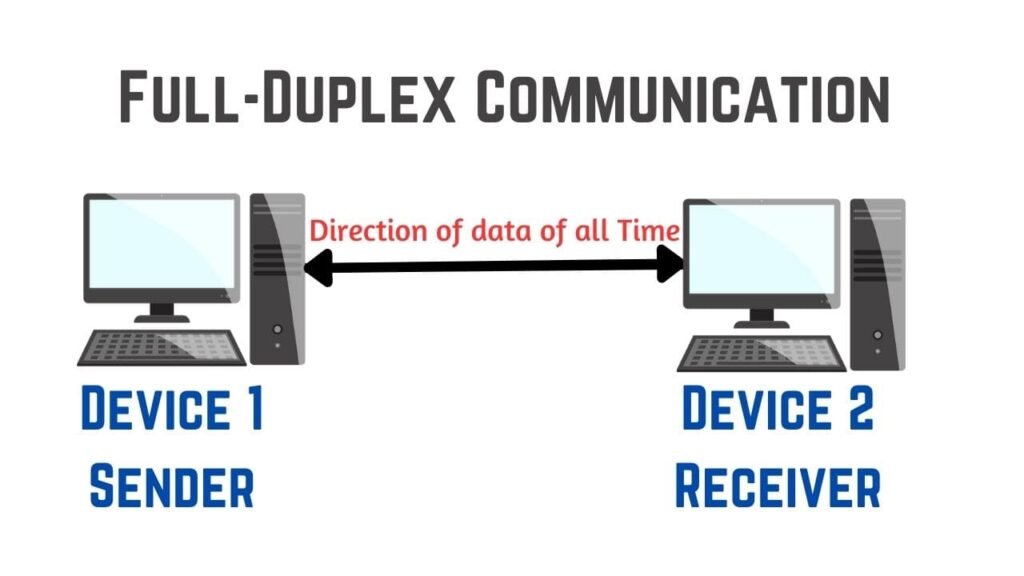
Full-Duplex Communication
It is exactly same as half-duplex communication but in this the sender send the data or message to the receivers and also the receivers receives the data at the same time. It is also known as two-way communication or bidirectional communication.
Example: Telephones lines and mobile phones etc.
Characteristics of Data Communication
There are four characteristics of data communication are:
- Delivery
- Accuracy
- Timeliness
- Jitter
Delivery
In the data communication, System must be deliver the data to the correct destination. It is known as Delivery .
Accuracy
At the time of delivering the data to its destination it must transferred accurately without getting any error. Sometimes the data may be corrupted during the transmitting which affects the accuracy level of transferring the data.
Timeliness
In the data communication, timeliness means the data must deliver on time without getting any delay, Late delivered data is useless It is known as “Timliness”. At the time of transmitting the audio/vedio file may takes times, but it doesn’t mean it is useless. The data of those file must takes a significant time not getting any extra time. It is also known as real-time transimission.
Jitter
It refers to the difference in packet arrival time. It is caused by an uneven delay in the delivery of audio or video packets.