Table of Contents
What is DNS
DNS stands for “Domain Name System” which is used to convert the domain name into its corresponding address, It is known as “DNS”. It is basically like a phonebook where all the phone numbers are recorded in it, Exactly the same as DNS provides a book where all the domain’s IP addresses are recorded in it and attached those IPs to its specific domain like: google.com, amazon.com, computerstudypoint.com, finobay.com, etc. well these domains are just a name so that people can easily learn it while surfing the internet.
Example: Suppose there is a website name: computerstudypoint.com and its corresponding IP is 198.102. 430.1. To connect this IP to this domain computerstudypoint.com, DNS is used to convert it and attach it and make a record in the server.
Who Invent DNS and when?

The concept of DNS was brought by an American computer scientist named “Paul Mockapetris” in 1983. The main motive to invent DNS is to provide identifiable names for IP addresses for website on the internet and makes the Internet far more accessible for everyday use.
How Does DNS Works?
While surfing a browser to get information from any website like you are getting information from our site, So when you enter our domain name into the search bar in the web browser that time you sent the request to the DNS server, and Now the DNS server takes your request and checks IP’s address on a DNS record. If the DNS server finds out the record then it will be sent to your browser so that you can able to access the website. So that’s the process of “How DNS works”.
Looks like the process is time-consuming, but no the process is done by the machine. As we all know how fast machines are 🙂
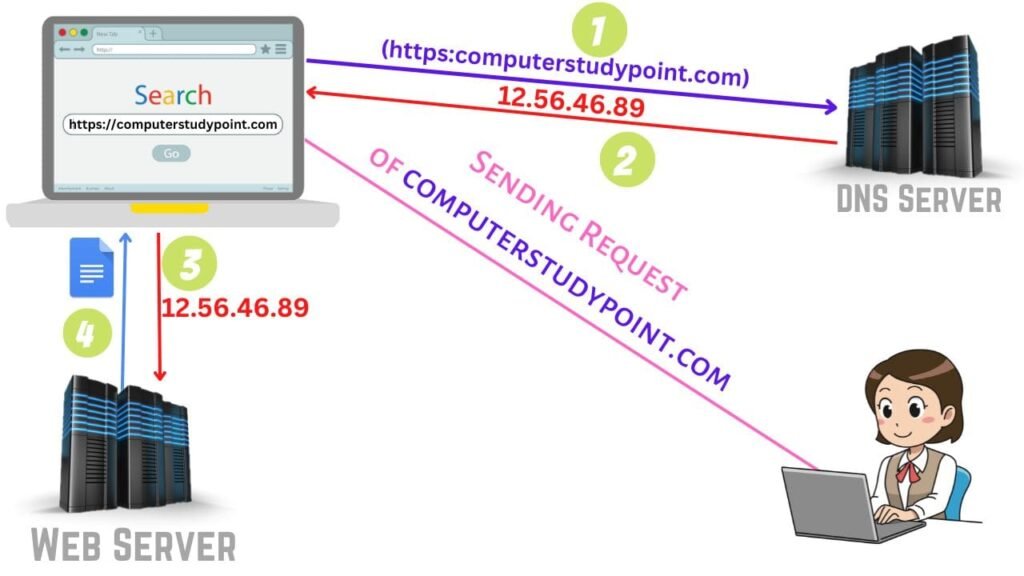
As you can see in the diagram a girl sends a request of computerstudypoint.com to the browser then:
- Step 1: It sends to the DNS Server
- Step 2: Then the web server checks the matching IP address in the record, when it finds outs then it sends it to the browser.
- Step 3: Now the browser sends those IP addresses to the Web server there web server provides the output to the screen.
- Step 4: As you can see web server sends a file to the web browser.
Types of Domain Names
If I talk about domains, there are so many types of domains available with the specific extension:
- .com
- .in
- .org
- .gov
- .net
- .edu
- and much more…
In DNS, there are three things that are important to understand: DNS Server, DNS Queries & DNS Records
Types of DNS Servers
- Root NameServers
- TLD NameServers
- Authoritative NameServers
- Recursive NameServer
1) Root NameServers
In the Domain Name System (DNS), a root name server is used to respond to the queries for each record in the root zone and answers other requests by returning a list. It is known as “Root NameServer”.
2) TLD NameServers
TLD nameserver is Top level domain nameserver that maintains all the information of all the top-level domains. TLD Domains example: .com, .org, .gov, .edu, .net, etc. In this nameserver, the information of all domains contains is known as “TLD NameServer”.
3) Authoritative NameServers
An authoritative name server is a server that provides an actual answer to your DNS queries is known as “Authoritative NameServers”
4) Recursive NameServer
Recursive DNS servers check the records obtained from the authoritative DNS servers for their corresponding IP address when users request the name of the website, It is known as “Recursive NameServer”.
Types of DNS Queries
- Iterative Queries
- Recursive Queries
- Non-Recursive Queries
1) Iterative Query
An iterative query is a DNS query when a user requests for the website to the name server (DNS resolver) then this query responds with a relevant answer to the user. It is known as an “Iterative Query”.
2) Recursive Query
In a recursive query, a resolver contacts a name server to do a name lookup, and the name server responds with a relevant result, It is known as a “Recursive Query”.
3) Non-Recursive Queries
In a Non-Recursive Query, The DNS Resolver already knows the solution When a query is made, the DNS records are immediately returned. It is known as a “Non-Recursive Query”.
Types of DNS Records
- A Record
- AAAA Record
- CNAME Record
- MX Record
- NS Record
- ANAME Record
- SOA Record
- TXT Record
- SRV Record
- PTR Record
- SPF Record
A Record
A record is an “Address Record” which is used to record the address of a specific IP address of a website to connect with the domain name. It is known as A record.
AAAA Record
AAAA record is used to match a domain name to an IP version 6 address. It is known as “AAAA record”.
CNAME Record
CNAME is a Canonical Name record where it provides an alias for another domain.
MX Record
MX record stands for “Mail Exchange Record”. It is responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain name. It is known as “MX Record”
NS Record
NS is a “NameServer Record” that contains the name of the authoritative name server within a domain or in a DNS zone.
ANAME Record
ANAME stands for “Alias Name” It is simply a record that functions like a CNAME record but at the root of your domain. It is known as “ANAME”.
SOA Record
SOA record is a “Starts of Authority Record”, In SOA it contains some crucial information about the domain name like the administrator’s email and more. It is known as “SOA”.
TXT Record
TXT is a “Text Record” that provides text information to sources outside your domain.
SRV Record
SRV is a “Service Record” It’s used to identify computers hosting specific services. It is known as “SRV Record”
PTR Record
PTR is a “Pointer Record” where It matches domain names with IP addresses and is used for reverse DNS lookups. It is known as “PTR record”.
SPF Record
SPF is a “Sender Policy Framework Record” which is used to identify the mail servers and domains that are authorized to send emails on the behalf of your domain. It is a SPF record.
